Introduction
Needs of people on the importance of getting information quickly and present a variety of growing. Various combinations of resources are used. Previously, in 1980s people began to get information through Internet but to very limited network. Latest, people can get various information at the fingertips through the use of mobile devices. To help researchers find a variety of sources and information, libraries and academic institutions should consider any methods and initiatives that the most efficient in providing variety of resources and information. Among the methods and initiatives that can be implemented by the library is to provide a platform for digital libraries and this digital libraries are also known as an open access initiatives. Previously, this initiatives is term as an Automated Library (Buckland, 1992) and Hybrid Library (Rusbridge, 1998). There are many definition of digital library by different researcher, library and information institution, as well as librarian and library professional. According to Waters (1998), Digital libraries are organizations that provide the resources, including the specialized staff, to select, structure, offer intellectual access to, interpret, distribute, preserve the integrity of, and ensure the persistence over time of collections of digital works so that they are readily and economically available for use by a defined community or set of communities. Moreover Suber (2004, 2007), defines digital libraries as an open access that “digital, online, free of charge and free of most copyright and licensing restrictions”. Many of open access repositories are set up by universities or research institutions to handle their own institutional research resources. Information about the trends and growth of open access repositories and journals are collated from monitoring initiatives comprising ROAR (Registry of Open Access Repositories), Open DOAR (Open Directory of Open Access Repositories), DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals) and Web Ranking of World Repositories by the Cybermetrics Laboratory in Spain.
In Malaysia, Academic Institutions and Library are competing each other to develop Digital Libraries or Open Access initiatives or also known as Information Repositories (IR). Most of the IR in Malaysian academic instituition and library are supply the information and full text of their own collection such as manuscript, thesis, journal article, conference proceeding, etc. In addition some of them are also put their picture album, article from newspaper, and collection of video about their university and library in their IR. The purpose of develop the IR is not only limited to just supply the information and resource material in their organisation but also as a knowledge sharing among others. Below, table 1 is show a list of Institutional Repository (IRs) across in Malaysia that listing in DOAR website.
In Malaysia, Academic Institutions and Library are competing each other to develop Digital Libraries or Open Access initiatives or also known as Information Repositories (IR). Most of the IR in Malaysian academic instituition and library are supply the information and full text of their own collection such as manuscript, thesis, journal article, conference proceeding, etc. In addition some of them are also put their picture album, article from newspaper, and collection of video about their university and library in their IR. The purpose of develop the IR is not only limited to just supply the information and resource material in their organisation but also as a knowledge sharing among others. Below, table 1 is show a list of Institutional Repository (IRs) across in Malaysia that listing in DOAR website.
Table 1 : List for Institutional Repositories (IRs) across Malaysia
No
|
Institutional Repositories
|
Host
|
Software
|
Collection type
|
Accessibility
|
1
|
.MyManuskrip: Digital Library of Malay Manuscripts
|
Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology, University of Malaya (UM), Malaysia
|
Greenstone
|
Books; Multimedia
|
Full Access
|
2
|
DSpace@UM
|
Faculty of Computer Science & Information Technology, University of Malaya (UM), Malaysia
|
DSpace
|
Conferences; Theses; Books
|
Restricted Access
|
3
|
ePrints@USM
|
Universiti Sains Malaysia, Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses; Unpublished
|
Restricted Access
|
4
|
PTSL UKM Repository
|
Perpustakaan UKM, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences
|
Restricted Access
|
5
|
UKM Journal Article Repository
|
National University Of Malaysia Library, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles
|
Full Access
|
6
|
UM Digital Repository
|
University of Malaya (UM), Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences; Multimedia
|
Restricted Access
|
7
|
UniMAP Library Digital Repository
|
The Library, Universiti Malaysia Perlis, Malaysia
|
DSpace
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses; Learning Objects; Multimedia; Special
|
Restricted Access
|
8
|
Universiti Putra Malaysia Institutional Repository (PSAS IR)
|
Universiti Putra Malaysia, Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses; Learning Objects; Multimedia; Special
|
Restricted Access
|
9
|
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Institutional Repository (UTM Institutional Repository)
|
UTM Library (Perpustakaan Sultanah Zanariah), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM), Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses; Unpublished; Books
|
Full Access
|
10
|
UNITEN (University Tenaga Nasional Digital Repository)
|
University Tenaga Nasional, Malaysia
|
DSpace
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses; Books; Learning Objects; Special
|
Restricted Access
|
11
|
UTHM Institutional Repository
|
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM), Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses; Books
|
Full Access
|
12
|
UUM IRepository
|
Universiti Utara Malaysia, Malaysia
|
EPrints
|
Articles; Conferences; Theses
|
Restricted Access
|
13
|
WorldFish Center Publications
|
The WorldFish Center, Malaysia
|
Articles; References; Conferences; Unpublished; Books; Special
|
Full Access
|
To explain in more detail relating to the development or digital library initiative, I will take the example of Australasian Digital Theses Program (ADT) to show the purpose of the digital library initiatives, thier target user community, subject or domain, collection and content including colection size, source document types, source document formats, metadata used for object description, access interface features (browse, search and display), technology aspects (e.g software used, database system, special h/w, and etc.
Purpose and Aim of ADT programme
· To establish a distributed database of digital versions of theses produced by the postgraduate research students at Australian universities.
· The theses will be available worldwide via the web. The ideal behind the program is to provide access to, and promote Australian research to the international community.
v The initial project was funded by an Australian Research Council (ARC):
Research Infrastructure Equipment and Facilities (RIEF) Scheme grant (1997/1998).
The original ADT membership group:
· University of New South Wales (lead institution)
· University of Melbourne
· University of Queensland
· University of Sydney
· Australian National University
· Curtin University of Technology
· Griffith University
Ø The ADT concept - initiative of 7 Australian universities in association with the Council of Australian University Librarians (CAUL).
Ø 1998-1999 -The ADT model was developed by the 7 original project partners.
Ø July 2000 -The program was then opened up to all CAUL members (all Australian universities).
Ø The original 7 partners will continue to guide and advise the national group in their role as the ADT Steering Committee.
 |
(1) User Interface – Common Web Browser
|
 |
(2) Enhanced access - search engines and free association of terms; hypertext linking
|
 |
Search Types:
– Basic Search
– Advanced Search
– Latest Search (History)
|
 |
hypertext linking
|
 |
(3) MetaData
|
 |
Fulltext available
(80% free access)
|
 |
Browse:
- Author
- Title
- School/Department
|
 |
(5) Value-added Services
(i) Search Tips
|
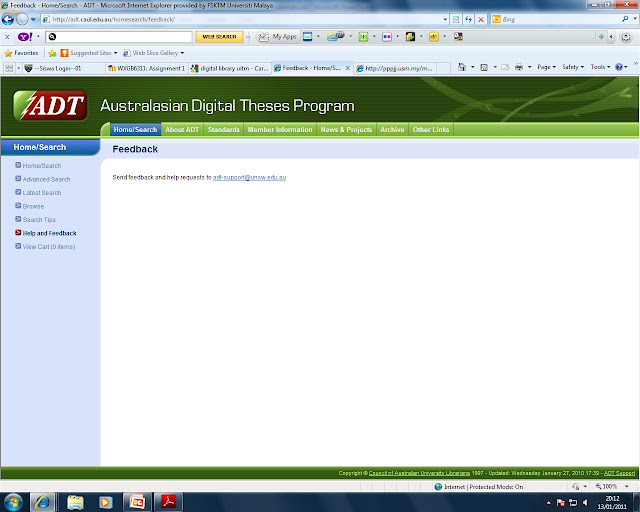 |
(ii) Feedback
|
 |
(iii) Standards
|
 |
(iv) View cart (selected records)
|
 |
(iv) View cart (selected records)
|
References
Buckland, M. (1992), Redesigning Library Services: A Manifesto, American Library
Association, Chicago, IL.
Rusbridge, C. (1998), “Towards the hybrid library”, D-Lib Magazine, Vol. 4 No. 7, pp. 40-5,
available at: www.dlib.org/dlib/july98/rusbridge/07rusbridge.html
Suber, Peter. (2004). Open access overview : focusing on open access to peer-reviewed
research articles and their preprints. http://www.earlham.edu/~peters/fos/overview.htm.
Waters, D.J. (1998). What are digital libraries? CLIR Issues, July/August. URL:http://www.clir.org/pubs/issues/issues04.HTML

No comments:
Post a Comment